SSL in the server
For have SSL in HTTP known as HTTPS first you need to have HTTP service.
For have HTTPS you need a certificate to expose that your domain is secure and you are your owner.
Now we are to explain how to generate your certificate for do a illustrative example, but in the practice the SSL certificate is created by Certification Authority (CA) that typically are companies of hosting. Remember this.
The CA establishes a chain of trust between he and domains of users:
About what your need in your server we use openssl that is typically installed in UNIX systems by default.
The process is divided in two steps: First need to generate the CA autosign for the server and later generate the clien certificate and sign it with serve CA.
Typically an SSL Certificate will contain your domain name, your company name, your address, your city, your state and your country. It will also contain the expiration date of the Certificate and details of the Certification Authority responsible for the issuance of the Certificate. When a browser connects to a secure site it will retrieve the site's SSL Certificate and check that it has not expired, it has been issued by a Certification Authority the browser trusts, and that it is being us.
CA Certificate in the server
first need to know OpenSSL directory. In terminal type:
openssl version -d
And report you the directory, typically usr/lib/ssl. Now we need to edit openssl.cnf and update this entries with your values. In my case this are my values:
....
[ CA_default ]
...
dir = ./demoCA
countryName_default = ES
stateOrProvinceName_default =
0. organizationalName_default = UMU
organizationalUnitName_default = ST
...
because my domain is a Spanish domain and the domian for the exmaple is st@um.
Now go to adjust options to generate a certificate. in the same file and go to [ policy_match ] section and update set stateOrProvinceName value to optional.
Go to the path of CA_default and create demoCA folder with this structure:
cd $HOME
mkdir -p demoCA && cd demoCA
mkdir -p newcerts
mkdir -p certs
touch index.txt
echo "00" > clrnumber
echo "01" > serial
Now you are ready to generate the certificate. To do it, run the appropriate command:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout cakey.pem -days 3650 -out
cacert.pem
You can check that your certificate is correct with this commands:
openssl x509 -in cacert.perm -text
openssl rsa -in cakey.perm -text
CA Certificate in the client
First generate it:
openssl req -new -nodes -newkey rsa:1024 -keyout serverkey.pem -out servercsr.pem
And later sign it:
openssl ca –keyfile cakey.pem -in servercsr.pem -out servercert.pem
The certificate on *.pem is necessary because is the format that the browser can read the certificate.
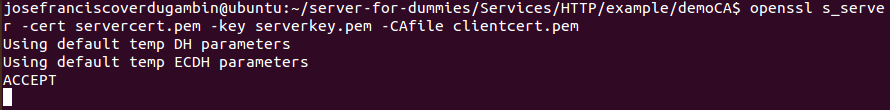
You can check that certificate is valid running this command:
openssl s_server -cert servercert.pem -key serverkey.pem -CAfile clientcert.pem